Publication Page Pre-print Online Appendix Data & Code
Abstract
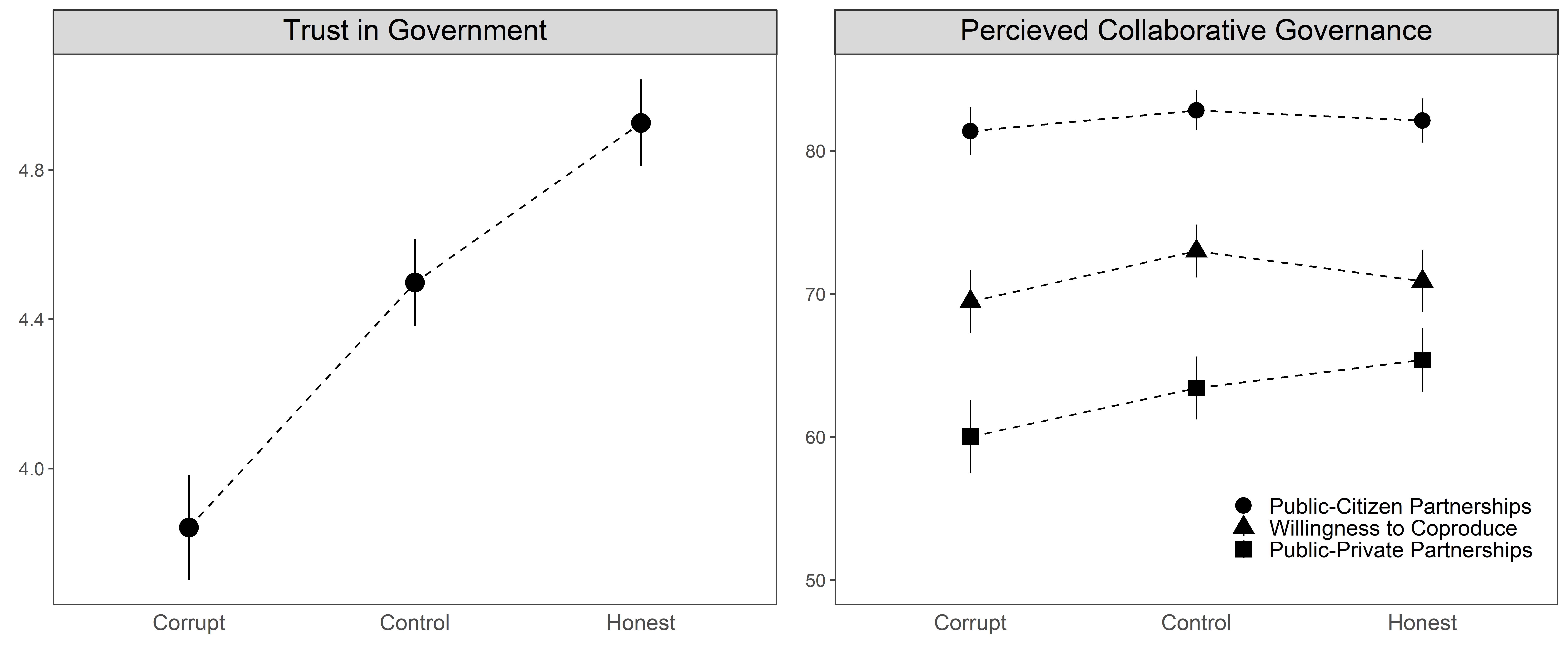
This research investigates the effects of trust in government on citizens’ perceptions of collaborative governance. To overcome endogeneity of measuring trust in traditional surveys, I proposed an alternative design that uses randomly assigned public integrity information as the instrumental variable of trust in government. The results from two online experiments indicate that citizens have strong preferences on public-citizen partnership, regardless the variations of trust in government. Moreover, trust in government has nonlinear effects on perceived public-private partnership and willingness to coproduce. These findings provide new opportunities to study public trust and offer implications to further develop collaborative governance theory.
Figure 3: Trust in government and perceived collaborative governance by experimental conditions in Study 2. Bars are 95% confidence intervals.